Read a single coordinate or axis rotation
This how to demonstrates how to read a single coordinate (X, Y, Z, RX, RY or RZ) or axis rotation (Base, Shoulder, Elbow, Wrist 1, Wrist 2 or Wrist 3) to be manipulated or worked with in the program.
Examples are valid for:
CB2 Software version: 1.8.16941
CB3 Software version: 3.1.17779
e-Series Software version: All versions
Note that older or newer software versions may behave differently.
Read a single coordinate or axis rotation:
The TCP position of the robot or the actual joint rotations may be used for many applications, and defines the basic terminology used to extract single parameters from a position variable (pose) or joint position (list).
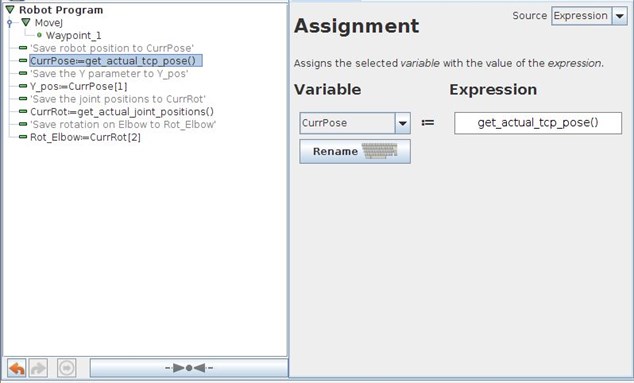
The actual positions of the robot can be read using the Assignment command, with these two functions:
get_actual_tcp_pose() – this function saves the current TCP position of the robot in the form p[x,y,z,rx,ry,rz].
This is called a pose variable, and the units of x, y and z are in meters while rx, ry and rz are axis angle positions in radians.
get_actual_joint_positions() – this function saves the current joint positions of the robot in the form [base, shoulder, elbow, wrist 1, wrist2, wrist3].
All units are in radians.
In order to read one of the values and save them as a single variable, this could be done:
Variable1 = get_actual_joint_positions()
Variable2 = Variable1[n]
n = 1 gives base rotation saved to Variable2.
n = 1 gives shoulder rotation.
n = 2 gives elbow rotation.
n = 3 gives wrist 1 rotation.
n = 4 gives wrist 2 rotation.
n = 5 gives wrist 3 rotation.
Same thing goes for the Cartesian TCP position, where the individual values can be saved as:
Variable3 = get_actual_tcp_pose()
Variable4 = Variable3[n]
Where:
n = 0 gives the X position in meters.
n = 1 gives the Y position in meters.
n = 2 gives the Z position in meters.
n = 3 gives the RX position in radians.
n = 4 gives the RY position in radians.
n = 5 gives the RZ rotation in radians.
All are relative to the Base coordinate system.
See example below: