
TCP/IP socket communication via URScript
Using a socket communication using TCP/IP
Examples are valid for:
CB3 Software version: 3.1
e-Series Software version: All versions
UR robot can communicate with outside equipment through TCP/IP protocol. In this article, we will introduce how robot can communicate with PC ,Robot will be the Client using URScript and PC will be the server.
Now, we will write C# code with VS2010 running in PC as the server listening client, Server’s IP is local 127.0.0.1,Port is 21.Then start the client with SocketTest. Otherwise we will also start the client as an example in the Polyscope.
Server: See attached URServer.zip
URSerever is modified by Visual Studio 2010 C#, this is a console solution.
C# code: See below and attached
| using System; using System.Net; using System.Net.Sockets; using System.Text; namespace URServer { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { // The IP address of the server (the PC on which this program is running) string sHostIpAddress = "127.0.0.1"; // Standard port number int nPort = 21; // The following names are used in the PolyScope script for refencing the // three working points: // Name of an arbitrary work point 1 const string csMsgPoint1 = "Point_1"; // Name of an arbitrary work point 2 const string csMsgPoint2 = "Point_2"; // Name of an arbitrary work point 3 const string csMsgPoint3 = "Point_3"; Console.WriteLine("Opening IP Address: " + sHostIpAddress); IPAddress ipAddress = IPAddress.Parse(sHostIpAddress); // Create the IP address Console.WriteLine("Starting to listen on port: " + nPort); TcpListener tcpListener = new TcpListener(ipAddress, nPort); // Create the tcp Listener tcpListener.Start(); // Start listening // Keep on listening forever while (true) { TcpClient tcpClient = tcpListener.AcceptTcpClient(); // Accept the client Console.WriteLine("Accepted new client"); NetworkStream stream = tcpClient.GetStream(); // Open the network stream while (tcpClient.Client.Connected) { // Create a byte array for the available bytes byte[] arrayBytesRequest = new byte[tcpClient.Available]; // Read the bytes from the stream int nRead = stream.Read(arrayBytesRequest, 0, arrayBytesRequest.Length); if (nRead > 0) { // Convert the byte array into a string string sMsgRequest = ASCIIEncoding.ASCII.GetString(arrayBytesRequest); Console.WriteLine("Received message request: " + sMsgRequest); string sMsgAnswer = string.Empty; // Check which workpoint is requested if (sMsgRequest.Substring (0,7).Equals(csMsgPoint1)) { // Some point in space for work point 1 sMsgAnswer = "(0.4, 0, 0.5, 0, -3.14159, 0)"; } else if (sMsgRequest.Substring(0, 7).Equals(csMsgPoint2)) { // Some point in space for work point 2 sMsgAnswer = "(0.3, 0.5, 0.5, 0, 3.14159, 0)";; } else if (sMsgRequest.Substring(0, 7).Equals(csMsgPoint3)) { // Some point in space for work point 3 sMsgAnswer = "(0, 0.6, 0.5, 0, 3.14159, 0)"; } if (sMsgAnswer.Length > 0) { Console.WriteLine("Sending message answer: " + sMsgAnswer); // Convert the point into a byte array byte[] arrayBytesAnswer = ASCIIEncoding.ASCII.GetBytes(sMsgAnswer+'\n'); // Send the byte array to the client stream.Write(arrayBytesAnswer, 0, arrayBytesAnswer.Length); } } else { if (tcpClient.Available == 0) { Console.WriteLine("Client closed the connection."); // No bytes read, and no bytes available, the client is closed. stream.Close(); } } } } } } } |
Client program
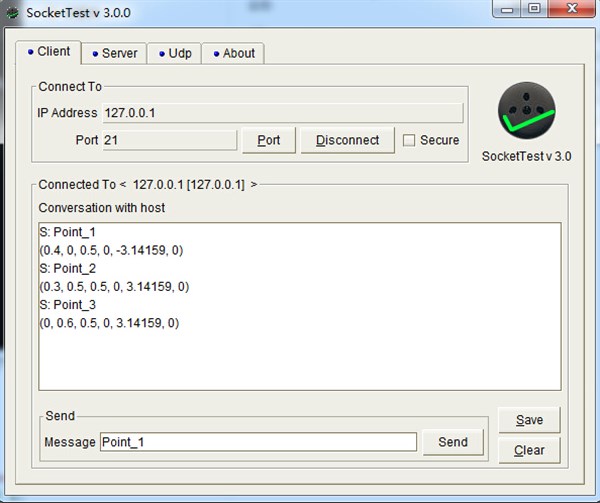
Firstly, start the server, then connect the client. Server will send client data ,once server receive the data from clent. Here Server can only receive “Point_1”,”Point_2” and “Point_3”.
Let us start the client in Polyscope next.
Program:
|
Program |
Please pay attention, if we using URScript “socket_read_ascii_float” to receive the data, the data format sent from server to client in Polyscope is strict.
1.The data must be surrounded by bracket pair
2.Every data unit must be split by comma
3.Must add ‘\n’ as the terminator
In this case, when enter “Point_1” in the Polyscope, then send to server, server will send back "(0.4, 0, 0.5, 0, -3.14159, 0)"+’\n’. Using URScript “socket_read_ascii_float(6)” to receive data from server. Normally,receiveFromServ will be “[6,0.4, 0, 0.5, 0, -3.14159, 0]”. receiveFromServ[0] means how many data unit is sent from server. We can take receiveFromServ[0] as the checking code.
Example: If server send “(0,0,0.1)”+’\n’, client will receive “[3,0,0,0.1]; If server send “(0.3)”+’\n’, client will receive “[1,0.3]”;