Pulse-Driven Tools
| Description |
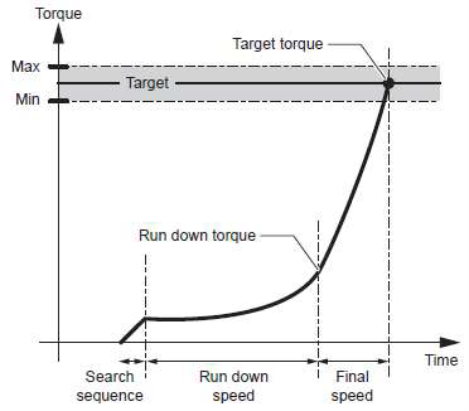
Most automatic screwdrivers and nut runners use continuous fastening techniques, in which the torque is increased continuously until the target is reached:
|
|
|
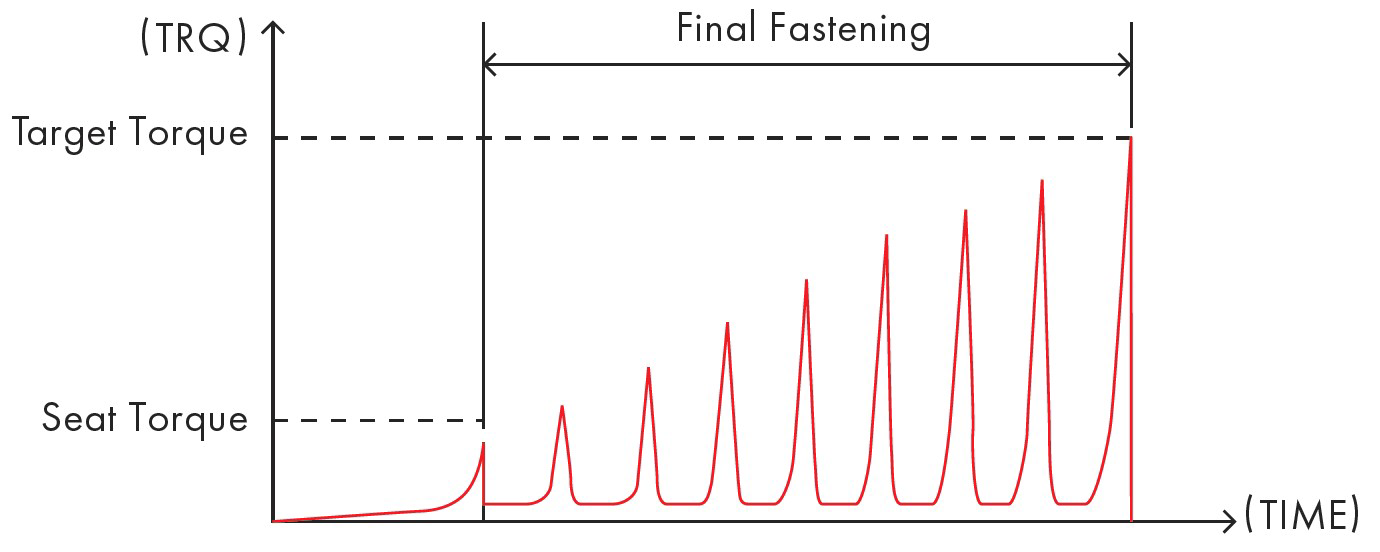
A smaller group of tools use pulse-driven fastening techniques, in which the torque reaction is smaller than in continuous fastening (some manufacturers claim reductions of up to 70-80 % with pulse-driven tools) by applying the torque in a sequence of increasing torque pulses as shown below:
Some pulse-driven tools can reach tightening torques up to 150 Nm – 180 Nm, but accuracy of this torque may not be as high as a continuous tool, so they might not be suitable for some processes.
There have been successful trials using pulse-driven tools mounted to UR10/UR10e robots tightening up to 140 Nm, but while reducing the torque reaction with a pulse-driven tool could be better for the robot, the vibrations associated with this technique should always be carefully observed.
For reference, the following list includes pulse driven models from multiple manufacturers:
|