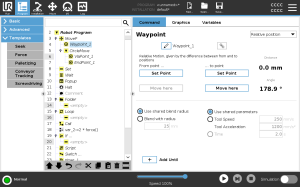
Relative Waypoint
| Example: Add relative waypoint |
To move the robot 20 mm along the z-axis of the tool: |
| Add a relative waypoint to a robot program |
|
| Detail |
The movement between two relative waypoints is always the shortest path for the robot depending on the move type. The distance for relative waypoints refers to the Cartesian distance between the TCP in the two positions. The angle states how much the TCP orientation changes between the two positions, or more precisely, the length of the rotation vector describing the change in orientation. It does not matter where the relative waypoint position was located around the robot, before the program moved into the relative waypoint. As soon as PolyScope moves to the relative waypoint in the program tree, the robot moves from its current position, to the distance and in the direction the relative waypoint has saved. Repeated relative positions can move the robot arm out of its workspace.
|
| Use Case: Welding and changing welding items
|
If you have a welding procedure, and you need to weld a seam around a rectangle, you can define the first corner with a fixed waypoint, and then make the robot and welding tool hit the remaining three corners using relative waypoints. The first waypoint will start the welding seam around the rectangle, and the relative waypoints will finish the remaining corners. Then if you need to weld something that is still a rectangle, but larger or smaller, then you can change the distance of the relative waypoints, and quickly modify the robot program.
|