Maximum Payload
| Description |
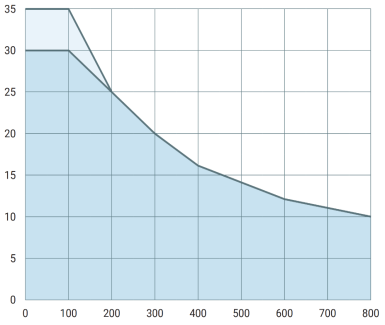
The rated robot arm payload depends on the center of gravity (CoG) offset of the payload, as shown below. The CoG offset is defined as the distance from the center of the tool flange to the center of gravity of the attached payload.
The robot arm can accommodate a long center of gravity offset, if the payload is placed below the tool flange. For example when computing the payload mass in a pick and place application, consider both the gripper and the workpiece.
The robot's capacity to accelerate can be reduced if the payload CoG exceeds the robot's reach and payload. You can verify the reach and payload of your robot in the Technical Specifications.
|
 expanded payload expanded payload
 full performance full performance
|
The relationship between the rated payload and the center of gravity offset.
|
| Payload capacity increase |
The robot arm can accommodate higher payloads and longer CoG offsets, if the payload is placed below the tool flange. You can increase the maximum payload capacity of the robot arm, under the following criteria:
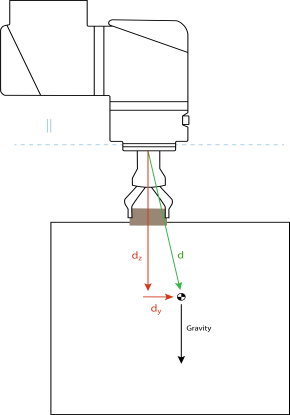
Example of how to compute the horizontal center of gravity offset.
As illustrated above, the horizontal payload offset dy should be within the payload curve.
Expanded payload is possible for any robot mounting orientation.
Increasing the maximum payload capacity can cause the robot to move at reduced speeds and lower acceleration. The higher load on the joints can limit some motions inside the working range of the robot. The robot software automatically ensures the mechanical limits of the robot are not exceeded. Using the expanded payload range does not void your robot warranty for this robot. |
| Payload inertia |
You can configure high inertia payloads, if the payload is set correctly. The controller software automatically adjusts accelerations when the following parameters are correclty configured:
You can use the URSim to evaluate the accelerations and cycle times of the robot motions with a specific payload.
|