Communication
| Description |
The Communication application allows you to monitor and set the live IO (input-output) signals from/to the robot control box.
|
|
Using the Communication application functionality |
|
|
To access Wired IO |
|
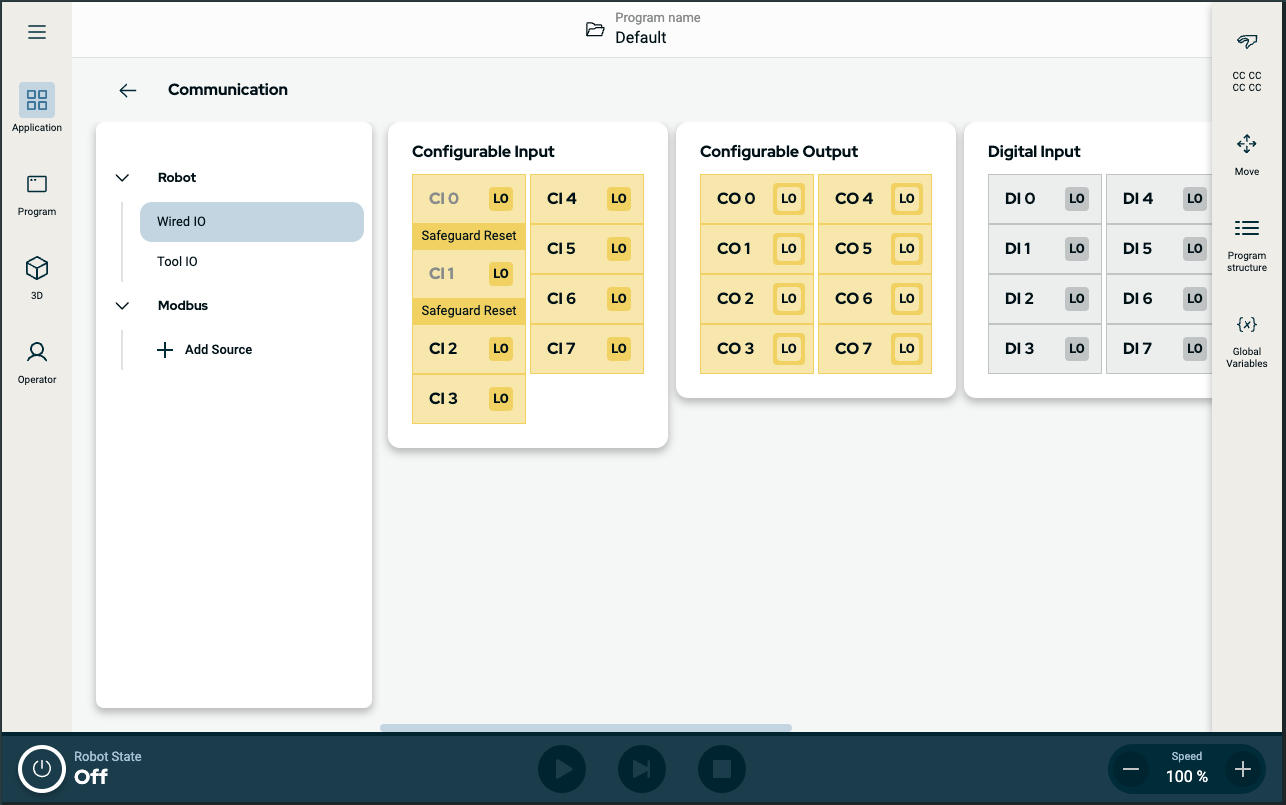
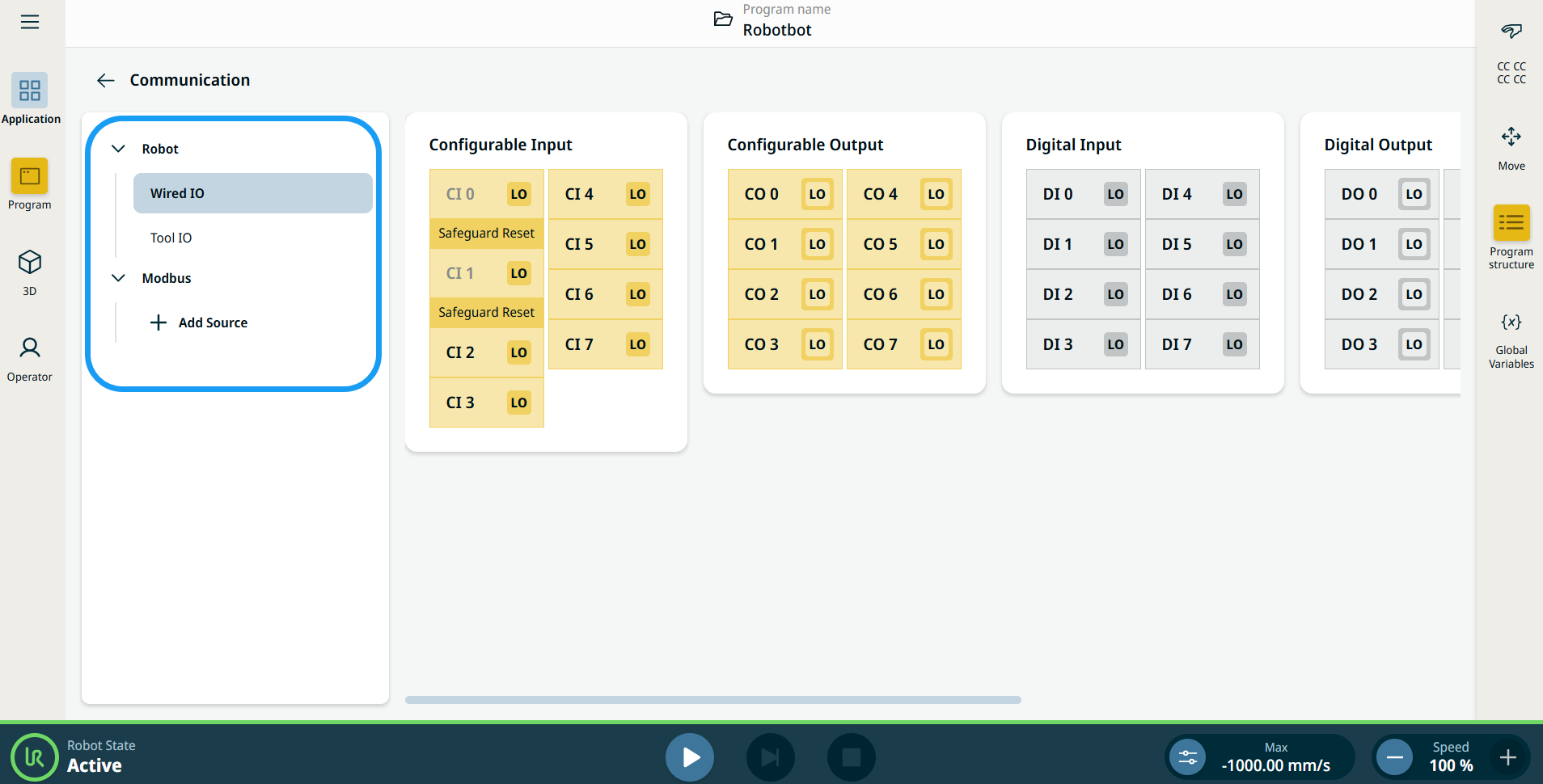
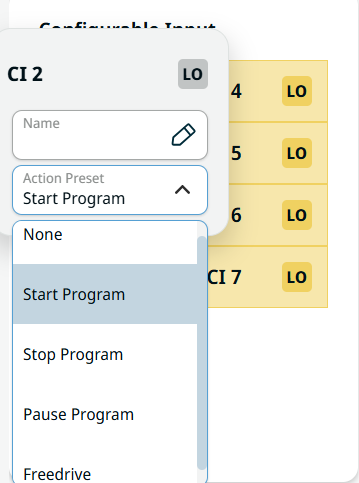
| Configurable Input |
Configurable input can be reserved for special safety settings defined in the IO Setup under Safety IO. Under those which are reserved for safety settings (CI 0 and CI 1), named Safeguard Reset, are in gray and cannot be edited. CI 2–CI 7 have editable fields. 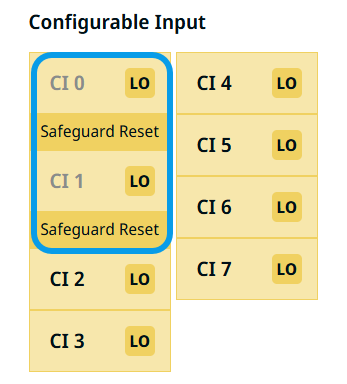
|
|
|
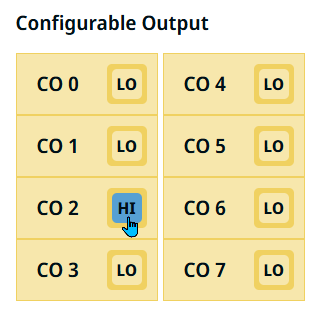
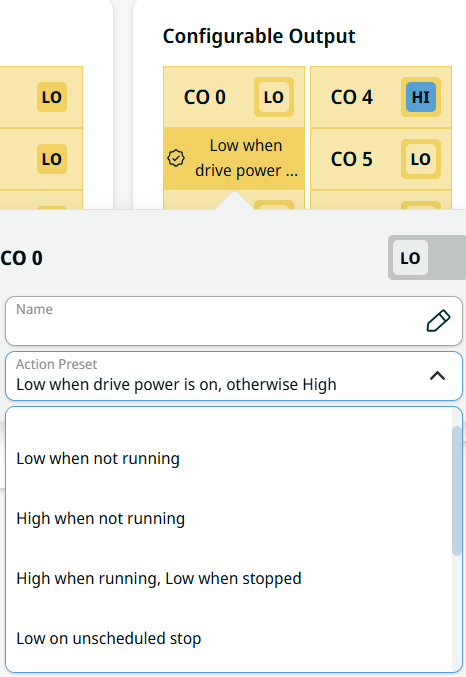
| Configurable Output |
The Configurable Output field ranges from CO 0 to CO 7.
|
|
|
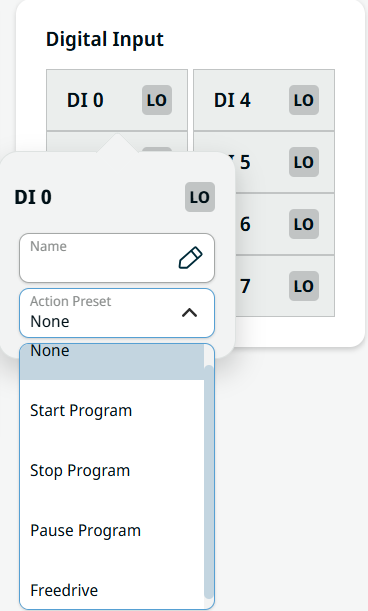
| Digital Input |
The Digital Input field ranges from DI 0 to DI 7.
|
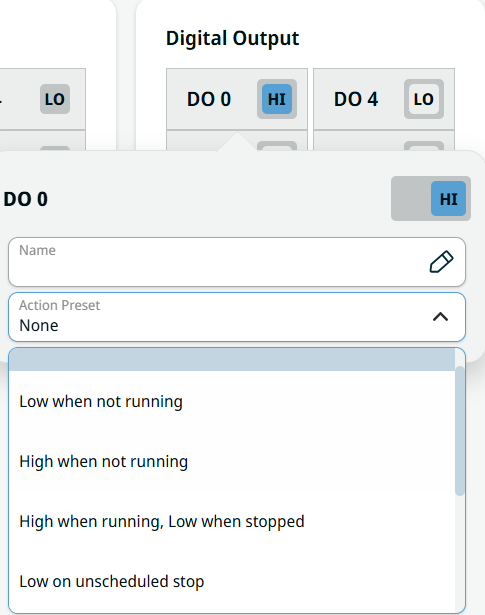
| Digital Output |
The Digital Output field ranges from DO 0 to DO 7 and are set independently to either high or low.
Follow all the steps as in Configurable Output. |
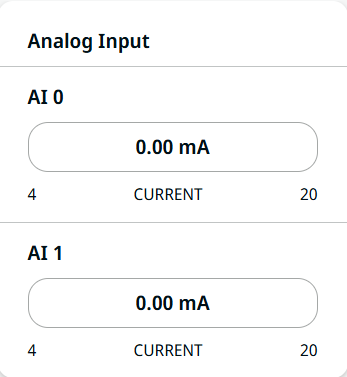
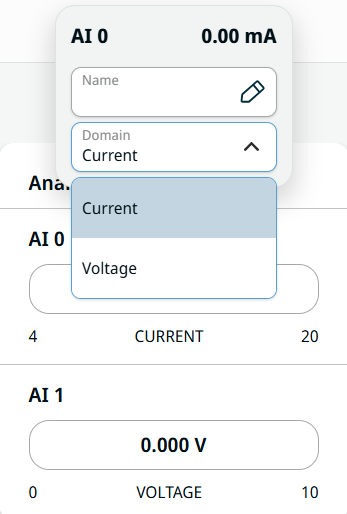
| Analog Input |
Analog input has two fields for AI 0 and AI 1. It can be set to 4–20 mA. These settings are persistent over restarts of the robot controller and saved in the installation.
|
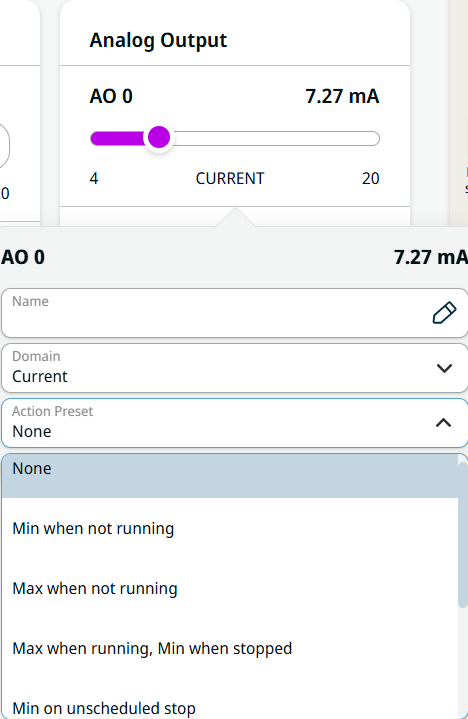
| Analog Output |
Analog output has two fields for AO 0 and AO 1. As with analog input, it can be set to 4–20 mA.
|
|
|
|
| To access Tool IO |
Tool IO monitors and sets the live IO signals from/to the control box.
Tap Tool IO on the left panel. You can see the editable fields of Tool Input and Tool Output on the right.
|
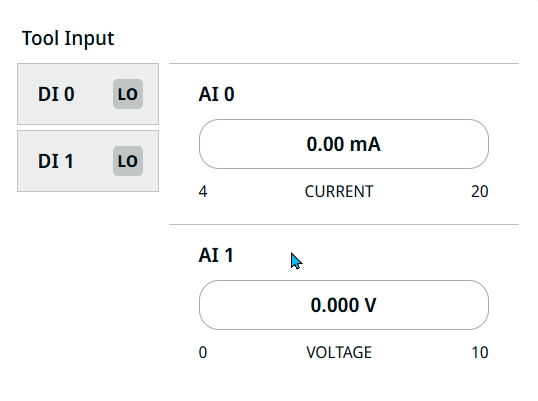
| Tool Input |
The Tool Input is composed of four fields:
|
|
|
|
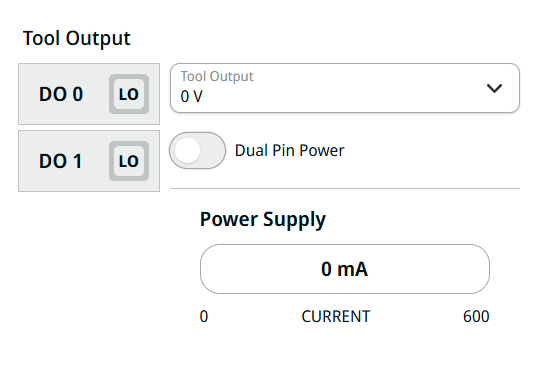
| Tool Output |
The Tool Output is composed of five fields:
|
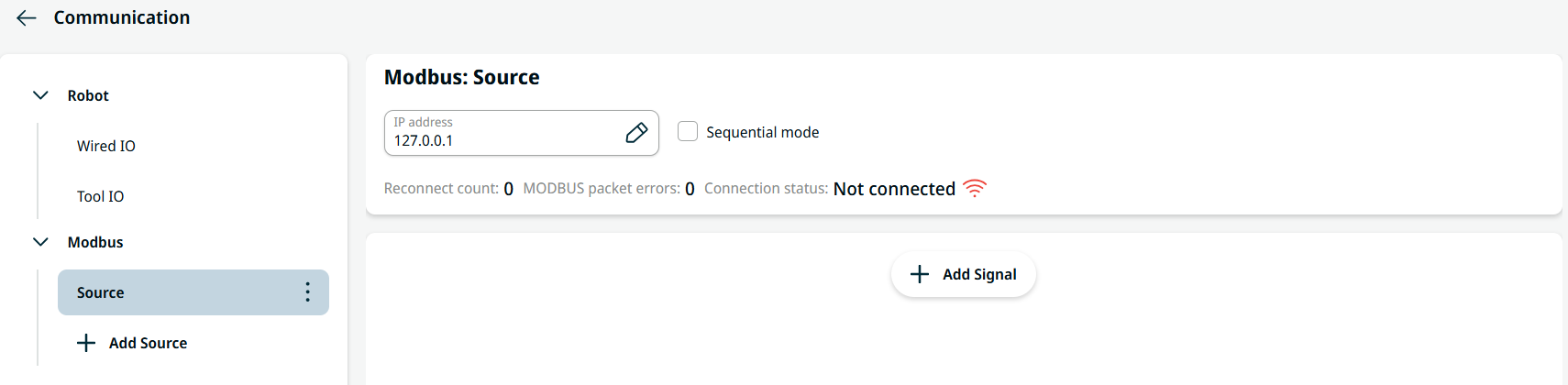
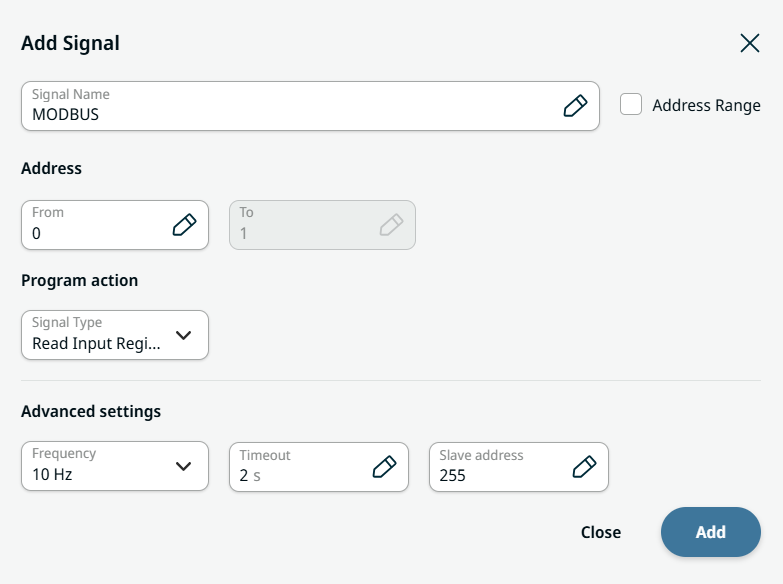
| Modbus |
Modbus is a serial communication protocol tied to a known IP address. It holds several input/output registers.
|
|